Energy conservation, emission reduction and environmental protection are one of the important links to ensure the implementation of China's national economy sustainable development strategy; it is also one of the goals of the heat treatment industry and heat treatment workers. As we all know, heat treatment is a major energy consumer and one of the major emitters and environmental pollution. In recent years, heat treatment equipment manufacturers and heat treatment workers have made a lot of efforts in equipment and technology, and have achieved certain results in energy conservation, emission reduction and environmental protection. The following is a summary of some of the work that Ipsen has done in recent years on energy conservation, environmental protection and environmental protection:
1 Super carburizing process
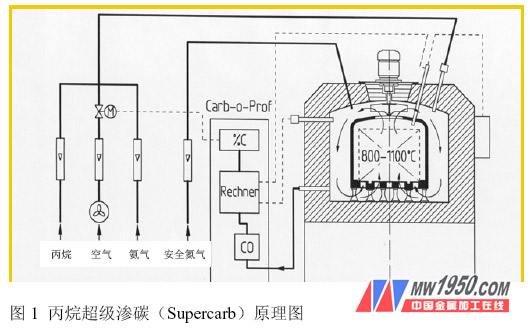
Based on the rapid development of computer technology, Ipsen developed the supercarb process in the 1980s and has been widely used in the next two decades. From multi-purpose furnaces, rotary hearth furnaces to mesh belt furnaces and pusher furnaces. This technology is continuously improved and more widely used and market recognized. Its working principle is shown in Figure 1. That is, the super carburizing process directly feeds the raw material gas and the air into the furnace, and cracks in the furnace to form a carburizing atmosphere. The feed gas inlet amount is fixed, and the carbon potential in the furnace is adjusted by adjusting the amount of air added, that is, when the carbon potential in the furnace is higher than the set value, the amount of air added is increased; When the carbon potential inside is lower than the set value, the amount of air added will be reduced. As the raw material gas, propane, acetone or natural gas can be optionally used.
The outstanding advantages of the super carburizing atmosphere are:
Energy saving:
A No need for air-conditioner, nitrogen generator and other ancillary equipment, less investment, reduce the shutdown caused by the failure of supporting equipment;
B carburizing speed is about 20%, the atmosphere is generated in the furnace, and the activity is good;
Gas
It can save 30~70% of raw material gas; it also reduces emissions.
2. Acetylene low pressure carburizing technology
Due to the thermal radiation effects of controlled atmosphere carburizing and the emission of exhaust gases, the process cannot be combined with mechanical processing
Come together. This is a far cry from today's integrated manufacturing technology philosophy. For decades, a process has been sought to replace conventional gas carburization. In the late 1960s, vacuum carburizing technology was developed and popularized in some areas in the 1970s and 1980s. During this period, the carburizing medium used for low pressure carburizing is generally propane, ethylene, and the like. However, the low-pressure carburizing process has not been widely applied because the following technical problems have not been solved. It can be said that in the past 20 years, low-pressure carburizing has been in the stage of research and development and trial production, and no industrial production has been formed. The main problems are:
a) Carbon black problem, which is a fatal flaw in the process. Because the carbon black deposited on the surface of the workpiece will cause uneven layer on the surface of the part; such as oil quenching after carburizing, it will lead to quenching oil contamination and unevenness of cooling; carbon black deposition on the surface of the heating electrode will cause short circuit Damage to the electrode; deposition of carbon black into the furnace chamber causes contamination of the furnace.
b) The problem of uniformity of the layer, in order to reduce the formation of carbon black, it is necessary to reduce the pressure or reduce the amount of gas introduced, which brings about the problem of poor uniformity of the layer. This is especially true for small parts that are densely packed.
c) The development of process procedures, process control and repetitive issues.
Until the mid-1990s, Ipsen developed a process of low-pressure carburization with acetylene, which revolutionized low-pressure carburizing technology. The above problems have been completely solved.
2.1 Cracking characteristics of acetylene
First look at the structural formula of acetylene:
HC ≡ CH
Acetylene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. The two carbon atoms are connected by a triple bond. The decomposition reaction of acetylene under vacuum and carburization temperature is as follows:
C2H2 2C + H2
This reaction is an endothermic reaction and relies on a metal surface. To sum up, the acetylene cleavage reaction has the following characteristics:
An acetylene molecule can decompose two carbon atoms;
The decomposition of acetylene is by means of a metal surface;
At the carburizing temperature, acetylene does not polymerize to form tar or the like.
From the above cracking characteristics of propane and acetylene gas, it is not difficult to see that acetylene has a more prominent advantage than propane as a carburizing medium. First, the amount of carbon available for acetylene is much larger than that of propane, which means that acetylene can be used as a carburizing medium at a very low pressure. In addition, acetylene has to be characterized by surface cracking of the workpiece, so acetylene low-pressure carburizing can eliminate carbon. The formation of black, and the carburization of complex geometric parts and even blind holes. Thereby solving the problem of uniformity of the layer and dense charging. There is no need to worry about the formation of tar in the furnace.
Next page
High Density Board,Density Fibreboard,Hdf Fiberboard,Hdf Panel Board
Linyi Fengzhize Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.fengzhize.com
