Recently, the research team of Zhang Yongsheng, a researcher of the Institute of Material Computation Science, Institute of Solid Physics, Hefei Academy of Material Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made new progress in the study of the effect of rattling effect on thermal conductivity in half-Heusler materials. Relation to thermal conductivity: Ordered half-Heusler semiconductors was published in Physical Review B.
The conversion efficiency of thermoelectric materials can be measured by the dimensionless ZT value, ZT = S2sT / κ, where S, s and κ represent Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, respectively. In the research of thermoelectric materials, it is very important to understand and analyze the factors that affect the thermal performance of semiconductors, which can provide a theoretical basis for reducing the lattice thermal conductivity of materials or developing materials with low lattice thermal conductivity. The phonon glass-electronic crystal (PGEC) concept states that high-performance thermoelectric materials should have a low thermal conductivity like glass and a high electrical conductivity like crystals; this requires materials to have independent electrical and thermal Yun grid. In general, frame materials containing rattling (near free vibration) atoms will exhibit similar PGEC characteristics as described above. Around this concept, many complex new compounds have been studied, such as cage clathrates and filled skutterudite materials. In recent years, Half-Heusler (HH) compounds have attracted much attention due to their excellent electrical properties, strong mechanical properties, and good thermodynamic stability. From the perspective of crystal structure, it contains three nested face-centered cubic substructures, which can be regarded as a filled sphalerite crystal structure. If one of the atoms is weakly bound to the surrounding neighbors, it is easy to vibrate in the face-centered cubic lattice, showing rattling behavior, which can effectively scatter phonons and reduce thermal conductivity. In this unique structure, studying the effect of rattling vibration behavior on thermal conductivity is of great significance for the design of HH materials with low thermal conductivity.
To this end, based on the phonon calculation of density functional theory method, the research team of Zhang Yongsheng's research group studied the effect of rattling vibration behavior in half-Heusler materials on thermal conductivity. It is found that thermal conductivity not only has a positive correlation with the average phonon frequency of the material, but also has a good positive correlation with the average effective spring constant between atoms. Further, they constructed two parameters that can succinctly measure thermal conductivity: the ratio of the smallest average phonon angular frequency to the largest phonon angular frequency (ωmin / ωmax) and the lowest effective spring constant and the highest effective spring constant of the three atoms Ratio (kmin / kmax). The calculation results show that the smaller the value of ωmin / ωmax, the weaker the bond between atoms; the smaller the value of kmin / kmax, the lower the rattling frequency. This calculation method can be used to determine materials with low lattice thermal conductivity simply and effectively, and helps to understand the relationship between rattling vibration in the material and low lattice thermal conductivity, and provides a method for screening potential low thermal conductivity materials. New ideas.
The above research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Hefei Branch of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Supercomputing Center.
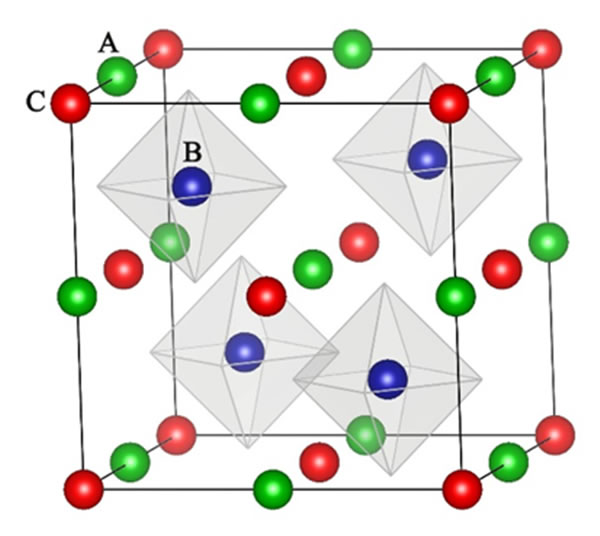
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the crystal structure of the Half-Heusler compound.
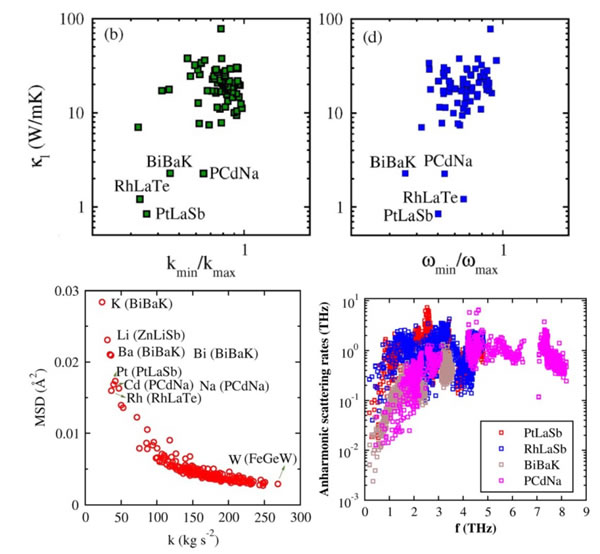
Figure 2. (a) Relationship between minimum and maximum effective spring constant ratio and thermal conductivity; (b) Relationship between minimum and maximum phonon angular frequency and thermal conductivity; (c) Spring constant and average effective displacement of each atom The relationship between the square of (d) the relationship between the phonon frequency and the anharmonic scattering rate of the four materials with lower lattice thermal conductivity.
We diviided the led light according to the using eviiroment. Most of our product is the commercial LED Lighting
Commercial lighting is a term used to describe lighting that is used in commercial spaces, including auto dealerships, distribution centers, churches, factories, offices, and warehouses. Unlike residential lighting, commercial lighting is made to withstand more abuse and has a longer lifespan.
While the focus of residential lighting is often on aesthetics, commercial lighting is task orientated. Commercial lighting systems are designed based on what the application is. For example, in an office-type setting, you may see task lighting, which illuminates specific areas where employees need concentrated light to be able to perform their jobs.
Flood Light,250W Led Flood Light,Led Flood Light 400 Watt,Led Flood Light Solar
Jiangmen Dilin Lighting High-Tech Co., Ltd. , https://www.jmdilinlighting.com
