The intersystem crossing from singlet state to triplet state is an important basic process of photophysics. At the same time, organic semiconductor materials with a large number of triplet states have broad application prospects in the fields of photovoltaic, room temperature phosphorescence and photodynamics. Therefore, designing and synthesizing triplet organic semiconductor materials is a hot topic in the field of materials, attracting widespread attention from scientists.
In the field of organic solar cells, the working mechanism of triplet materials has always had different scientific views. The early point of view is that triplet materials are conducive to increasing the exciton migration distance, which is conducive to the improvement of solar cell performance; recent related studies have shown that due to the presence of the triplet-triplet quenching (TTA) process, triplet materials may be Not conducive to exciton migration and charge separation, and thus not suitable for the construction of high-performance organic solar cells.
In response to the basic scientific issues of the triplet, the Huanghui Research Group of the College of Materials Science and Optoelectronics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Key Laboratory of Vacuum Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has taken porphyrin materials as an entry point in recent years and systematically studied the use of such triplet materials in the field of optoelectronics. Application to explore the basic working principle of triplet materials. The researchers designed and synthesized the first n-type porphyrin conjugated macromolecule material and constructed an excellent all-polymer organic solar cell (ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8, 34620-34629). Then, random copolymerization was used to design and synthesize a series of randomly copolymerized n-type conjugated polymer materials, and a highly responsive all-polymer photodetector was constructed (ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10, 1917-1924). However, in the above research process, due to the limitations of the material itself, no significant triplet state was observed. Therefore, the working mechanism of the triplet material has not been further studied.
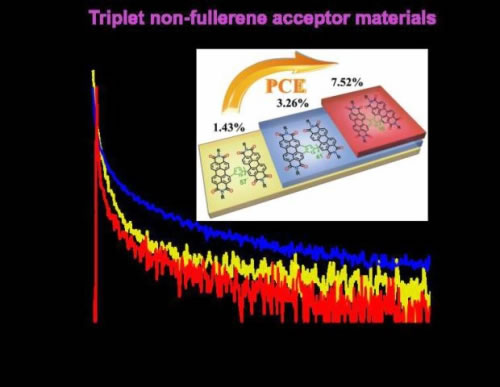
Recently, under the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Huang Hui's research group has designed and synthesized a series of styrene n-type organic semiconductor materials with different degrees of fused rings. The results show that the degree of fused ring has a significant impact on the physicochemical properties of the material and the performance of the solar cell; through the regulation of the degree of fusion ring, an organic solar cell with an energy conversion rate of more than 7.5% is finally realized. Further research shows that this type of material has a strong intersystem crossing, resulting in a large number of triplet states, which is conducive to increasing the exciton diffusion distance. At the same time, because the triplet energy level of this type of material is not lower than its charge transfer (CT) state, the triplet excitons can return to the charge transfer state and eventually be separated into free-moving electrons and holes, thereby benefiting the solar cell. Increased performance. The work was reviewed by the reviewers as "concept novelty and significance" and published on Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2018, 57, 1097).
Expanded metal is sometimes considered an alternative to sheet metal or wire mesh. It combines some of the best features of both-providing a material that is stronger than thin wire mesh and has better air flow and drainage than sheet metal.
Expanded Metal Mesh,Element Expanded Metal Mesh,Aluminum Expanded Metal Mesh,Ss Standard Expanded Metal Mesh
HEBEI KAYI BUILDING MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.kayigrating.com
